DFaaS: Decentralized Function-as-a-Service for Federated Edge
This repository holds DFaaS, a novel decentralized FaaS-based architecture designed to automatically and autonomously balance the traffic load across edge nodes belonging to federated Edge Computing ecosystems.
DFaaS implementation relies on an overlay peer-to-peer network and a distributed control algorithm that takes decisions on load redistribution. Although preliminary, our results confirm the feasibility of the approach, showing that the system can transparently redistribute the load across edge nodes when they become overloaded.
Our prototype is based on OpenFaaS and implements the control logic within Go P2P agents.
This research is conducted by the DatAI (formerly Insid&s) and REDS laboratories of the University of Milan-Bicocca.
If you wish to reuse this source code, please consider citing our article describing the first prototype:
@inproceedings{Ciavotta_DFaaS_2021,
author = {Ciavotta, Michele and Motterlini, Davide and Savi, Marco and Tundo, Alessandro},
doi = {10.1109/CloudNet53349.2021.9657141},
pages = {1--4},
series = {2021 IEEE 10th International Conference on Cloud Networking (CloudNet)},
title = ,
url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9657141},
year = {2021}
}
Scenario
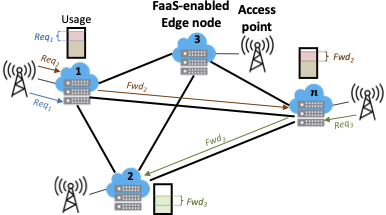
The above figure depicts the considered network scenario. A set of geographically-distributed FaaS-enabled edge nodes (or simply edge nodes) is deployed at the edge of the access network.
Each of these nodes deploys a DFaaS platform for the execution of serverless functions, and is connected to a wireless or wired access point (e.g. a base station, a broadband network gateway, a WiFi access point, etc.).
The edge node can receive functions’ execution requests, in the form of HTTP requests, generated by the users served by the access point.
Architecture
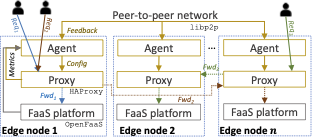
How to run DFaaS
DFaaS is currently in a prototypal stage. It uses HAProxy for the proxy component and OpenFaaS as the FaaS platform. The only supported deployment method is on Kubernetes.
You can install and deploy the DFaaS prototype on a single node using Ansible. This can be done either on the machine running Ansible or on a remote machine. See the dedicated section.
Or you can do a manual deployment: follow what the given Ansible playbook does and execute each required command step-by-step.
Regardless of which of the options you choose, the deployment of the DFaaS prototype has been tested with Ubuntu 24.04.2 LTS.
We suggest to spin up a virtual machine from scratch with Ubuntu, with a user with a password and sudo enabled.
Automated deployment with Ansible
Install Ansible on the control node following the official
documentation
(use the Ansible PPA). Then use the provided playbook
setup_playbook.yaml to deploy a DFaaS node on a
specific managed node specified in an inventory file. Note that you can specify
multiple managed nodes.
An example of inventory.yaml file is
all:
hosts:
<node-name>:
ansible_host: <ip_address>
ansible_user: <user>
ansible_password: <password>
ansible_become: true
We assume that the managed node has a user with root privileges and can connect via SSH with a password. This is for testing purposes only!
To test the inventory, you can try the example playbook on the official Ansible documentation.
Important: on the control node you need to have the DFaaS Git repository and to build the DFaaS Agent. This can be done with the following:
$ git clone https://github.com/unimib-datAI/dfaas.git
$ sudo apt install golang-go
$ go build -C dfaas/dfaasagent
Then you can run the playbook with ansible-playbook (make sure to be on the DFaaS directory!):
$ ansible-playbook -i inventory.yaml setup_playbook.yaml
This deploys a basic, fully functional DFaaS node using the Node Margin Strategy. See here for a list of available strategies for the agents.
You can make automatic calls to the node with k6. More information about it in the dedicated directory.
If you have four different VMs it’s recommended to deploy the entire system
exploiting the playbook and configuration files in
test_environment. This is still a work in progress.
Deploy functions
Use the k8s/scripts/deploy-functions.sh
script to automatically deploy the default functions to the local DFaaS
instance. If you use the Ansible playbook, this step is done automatically.
We also created a basic ML inference function for OpenFaaS named
image-classification. Refer to its
documentation for more details.
Invoke a function
Each node exposes HAProxy with port 30080 on the node’s IP address. Only
http protocol is supported. You can use any program to make a call, as
example:
$ curl -i http://127.0.0.1:30080/function/figlet -d 'Hello DFaaS world!'
In this case we assume that you have deployed the figlet function.
Forwarding traffic as a malicious node
You can impersonate a malicious node that is not part of the federation by
adding the header Dfaas-Node-Id with a value that is not a valid peer id of
the network (e.g., Dfaas-Node-Id: malicious-id). All of its requests will be
rejected.
Troubleshooting
See and follow the logs of the DFaaS Agent on the local instance:
$ POD=$(sudo kubectl get pods -l app=dfaas-agent -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
$ sudo kubectl logs --follow $POD
Emulator
Until commit 7a8512b, an emulator was available in the emulator directory, allowing multiple DFaaS edge nodes to be emulated on a single machine using Docker and Containernet. The emulator was removed when DFaaS migrated to Kubernetes (k3s), which requires a separate VM for each node. The recommended approach is now to run multiple VMs that can automatically connect on a hypervisor, which is the method we currently use.
Simulator
We also provide a simulator to test and compare different load balancing techniques. The simulation code is available into the simulation directory. Data gathered by the DFaaS system used for simulation are available here.
For more information read associated README file.
License
Copyright © 2021-2025 The DFaaS Authors.
The source code in this repository is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License (AGPL), version 2.0 or later. See the LICENSE file for more information.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Affero General Public License for more details.
The complete list of The DFaaS Authors can be fond in the AUTHORS file or in the contributors page on the DFaaS GitHub repository.